Overview
The Pak Accounting Fixed Assets program is designed to help organize and manage depreciation entries. Once you enter details about your assets, the system can calculate the depreciation entries based on the specific information entered. Amounts may be changed to review the effect on the calculations, and the G/L entries may be posted into the General Ledger.
The system can manage up to seven sets of books for depreciation entries. The first three, called G/L (General Ledger), TAX (Tax), and AMT (Alternative Minimum Tax) are set up by default. This enables you to maintain separate calculations for internal books, Federal taxes, and AMT (Alternative Minimum Tax) depreciation.
There are also over 30 pre-defined classes, such as AUTOMOBILE or REALESTATE, which are used to categorize similar assets based on an IRS class code. These classes cover most accounting situations but Pak Accounting will add additional classes, if needed, once the request has been made for a specific IRS class code to be maintained. The user may also add a “user defined” class code for situations that are not defined by an IRS class code.
Setup
•Set Chart of Accounts [F11]] for Asset account, Accumulated Depreciation account, Depreciation Expense account
•Create G/L Entries (if converting from another system)
•Once the setup is complete, please see the Reports section for all reporting options available.
Fixed Assets are depreciated in the system according to the method, life and convention defined for that asset. Each Asset may have up to 7 different books for recording the depreciation, however, only one of those books may be used to post entries to the General Ledger. The user must determine whether they want to post the GAAP depreciation (straight line – GL book) to their general ledger, or if they prefer to post the TAX or AMT book to their general ledger. In most cases, clients post the GL book or straight line method to the general ledger. However, we do have a few clients that prefer to post the TAX book to the General Ledger. At this time, there are not any known clients that are posting AMT book to the General Ledger. |
Overview and flow of Fixed Assets to and from the General Ledger Fixed Assets is an optional part of the General Ledger system. This module is used to create General Ledger entries to adjust the Net Book Value via the assets accumulated depreciation account(s). The Fixed Assets Module will import (if prompted) entries from the General Ledger to create new assets, but the user may set up the assets separately in the Fixed Assets module if they prefer the manual set up over importing. The entries that may pull into Fixed Assets from a General Ledger import may originate from Accounts Payable, Check Stub Cost, Revenue/Billing Investor Interface, or General Ledger entries (standard or manual). However, the majority of entries will come from the Accounts Payable module. These entries will establish the initial value of an asset. |
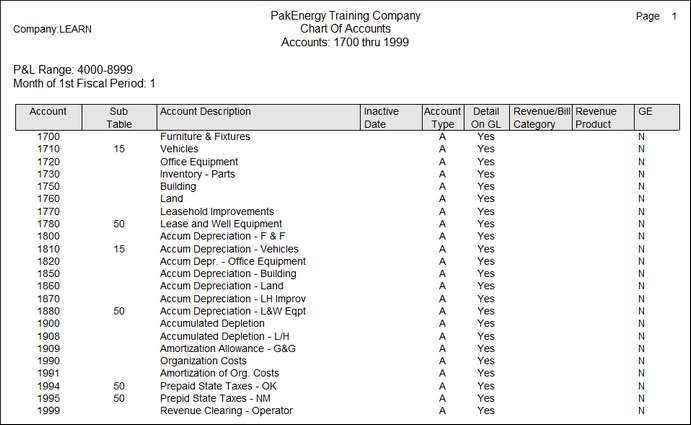
There are three different types of accounts that are needed for the Fixed Assets Module: 1.Asset Account(s) – Balance sheet account(s) that should have a debit balance to reflect the initial cost of an asset. These may or may not have a Sub-Table attached depending on preference and need. The Fixed Assets module will track the individual asset's cost, accumulated depreciation and net book value. The asset account only needs to have a Sub-Table attached when the separation is needed for financial reporting purposes. 2.Contra Asset Account(s) – Balance sheet account(s) that should have a credit balance to reflect the depreciation that has already been taken for a given asset. These are usually labeled as “Accumulated Depreciation” or “Accum Depr”. One Accumulated Depreciation account may be utilized for all assets or they may be split out into categories ie “Accum Depr – Office Equipment”, “Accum Depr – Automobiles”, etc. The only time multiple Accumulated Depreciation Accounts are required is when a user has multiple asset accounts that have different Sub-Tables attached to them AND the accumulated depreciation needs to be separated out by Sub-Table. Then, there is a need for an Accumulated Depreciation Account for each Sub-Table that is involved OR an accumulated depreciation account per asset account. Once again this is based on Financial Reporting preference, since the Fixed Assets Module will keep these calculations accurate at the asset level regardless of the detail showing at the General Ledger level. 3.Depreciation Expense Account(s) – Income Statement expense account that typically carries a debit balance. Pak Accounting only requires one expense account, but just like the “Accumulated Depreciation” accounts, multiple accounts are optional based on financial reporting needs. Things to keep in mind when determining the chart of account set up. The system allows movement of assets from one cost center to another within the same Sub-Table with ease. However, moving assets from one General Ledger account to another General Ledger account is not a recommended use of Pak Accounting Software. To track this properly the asset would need to be “disposed of” under the old account number and then, placed in service under the new account number which would cause an issue for tracking the accumulated depreciation of the particular asset. If the move is from one Sub-Account to another Sub-Account, the Fixed Assets module will be able to track the move between cost centers easily. 1.List assets together in the 1xxx account range, and then, list the contra assets (Accumulated Depreciation) accounts together in the 1xxx account range (larger numbers, so they naturally show up below the assets on the balance sheet) 2.List the asset account in the 1xxx account range, and then, list the contra asset (Accumulated Depreciation) account right after it in the 1xxx account range. Repeat this process until all Asset and Contra Asset accounts have been listed. Here is a sample of what the Asset Account and Contra Asset Accounts may look like:
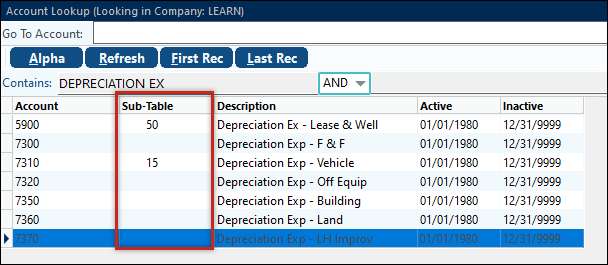
In this case the user wants to have the depreciation expense split out by cost center, too:
|
Pak Accounting Fixed Assets System Limitations & Notes 1.Automatically calculates the federal stimulus 80% bonus depreciation for 2023. Pak Accounting does maintain and support Section 179 annual caps (limitations on amounts). 2.Adjust basis for allowances based on rehab (handicap access equipment, etc). There is no separate field for this. 3.Most tax calculations can be computed within Pak Accounting using MACRS (Modified Accelerated Cost Recovery System) and/or AMT (Amount) depreciation. ACRS (Accelerated Cost Recovery System), ADS (Alternative Depreciation System), and ACE (Adjusted Current Earnings) depreciation methods are not supported. 4.Pak Accounting does not support/print any official IRS (Internal Revenue Service) tax forms, but does offer a tax report to facilitate the reporting of such tax information. Fixed Assets' main thrust is financial depreciation and reporting of assets, and providing a subsidiary of assets. 5.Disposal of fixed assets does not automatically flow into the Fixed Asset System from General Ledger, assets must be manually removed. Care must be taken that the two independent systems remain in balance as this is not an automatic, integrated procedure. 6.No Units of Production, Mileage based Depreciation, etc. 7.No % (percent) of use allowance, only 100% business use assets are supported. 8.Each asset is grouped into 3 accounts for making General Ledger entries: a fixed asset account, a fixed asset accumulated depreciation account, and an expense account. Currently those accounts must use the same Sub-Table or a blank Sub-Table. For example, you cannot sub out your fixed asset account by asset# (number), then sub out your expense account by cost center, each one of the three accounts must use either the same Sub-Table or a blank Sub-Table.
|
Also see: